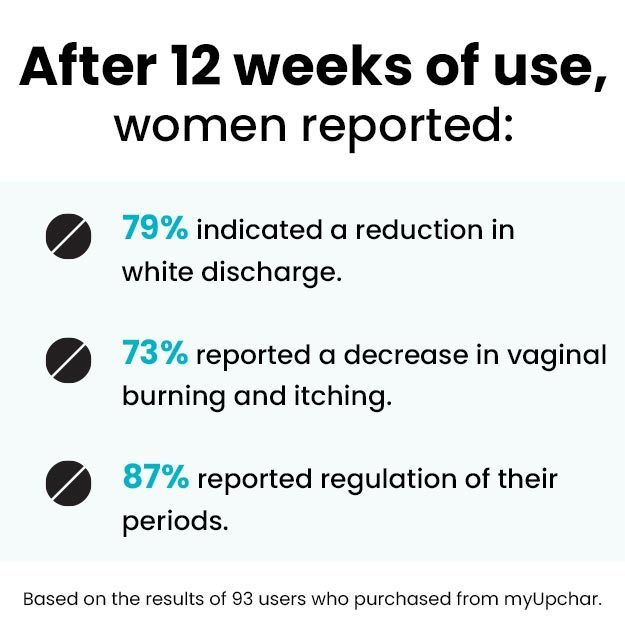
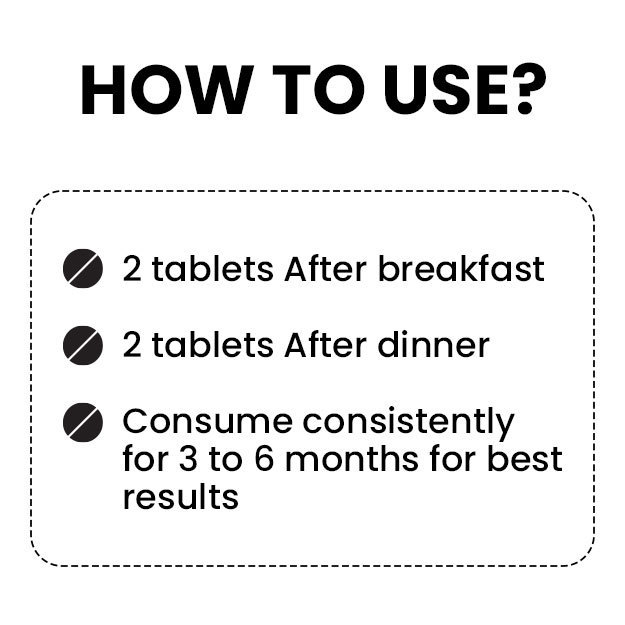
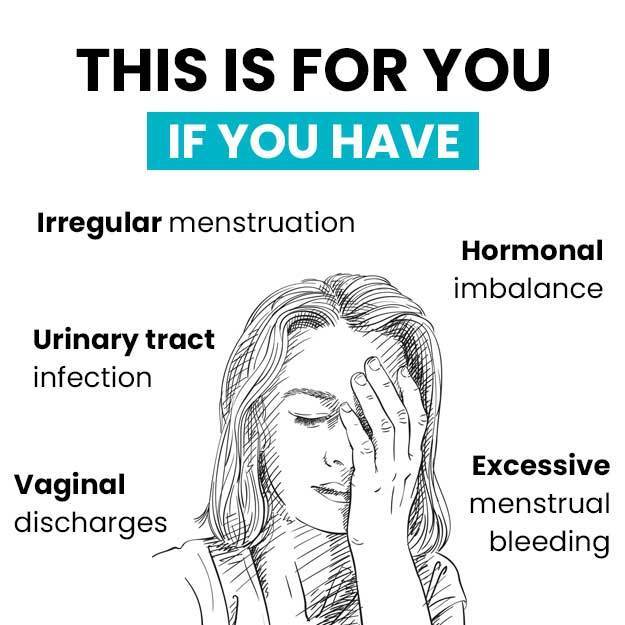
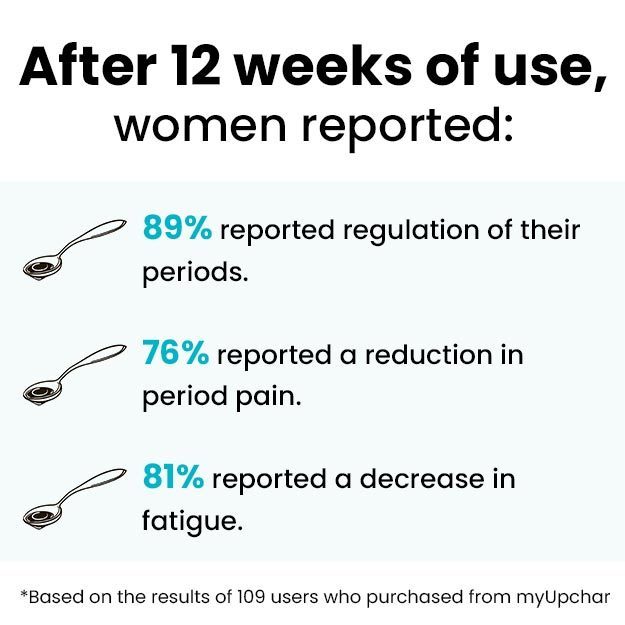
Menstruation is a normal hormonal mechanism of the body, which is periodically experienced by women in the form of a vaginal bleed. This occurs due to the failure of implantation following an ovulatory cycle and is indicative that the woman is not pregnant but is fertile.
Despite this known science behind menstruation, there are several myths and notions, especially in the Indian society making it much of a taboo. Due to this, women are often unable to talk about their menstruation-related problems openly and as a result, their health suffers.
It is imperative that these myths be busted so that women of the reproductive age are able to discuss their issues and seek medical help accordingly.
This article will introduce you to these myths and reinstate the facts so that you understand how menstrual cycle actually works. So, let’s get started.