Usually, hair fall does not require specific medical therapy. If significant loss is present though, the underlying cause should be investigated and, after arriving at an accurate diagnosis, should be treated adequately. Hair replacement therapy can be opted for by patients for cosmetic reasons to boost their self-esteem and confidence levels. However, it should be done after taking into consideration all the pros and cons of the procedure as it is not medically necessary and purely an elective cosmetic procedure that can be expensive.
(Read more: Food habits to stop hair loss)
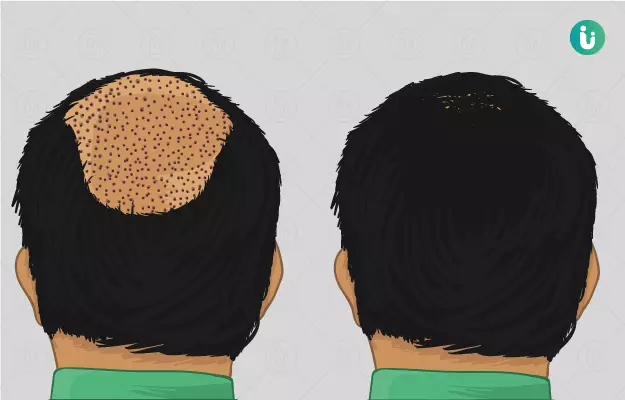
Hair transplantation is a surgical technique that involves removing hair follicles from one part of the body (the donor site) and implanting them in another (recipient) site, typically the scalp. Hair transplant is commonly used to cosmetically treat and correct male pattern baldness and receding hairlines but can also be used for eyebrows, arms, legs and even genital areas. Hair transplantation procedures can be opted for after consultation with a specialist surgeon and assessment of any contraindicating factors. Hair fall transplant is of two types – follicular unit transplantation (FUT) or follicular unit extraction (FUE). Both methods use different techniques to harvest the follicles of hair and transplant them to new sites. Precautions should be adhered to strictly and after-care medication should be taken diligently. Certain complications can arise due to the surgery or the drugs prescribed after it. Other options for hair loss management can be discussed and considered beforehand.
(Read more: Hair loss prevention and natural remedies)