Summary
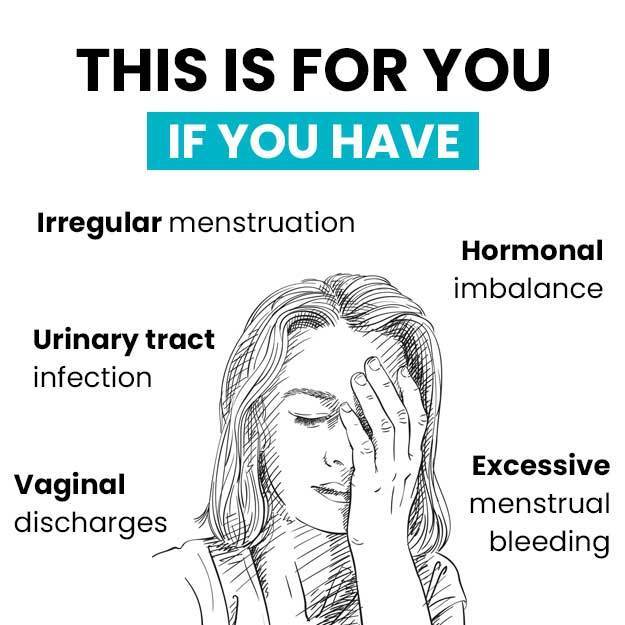
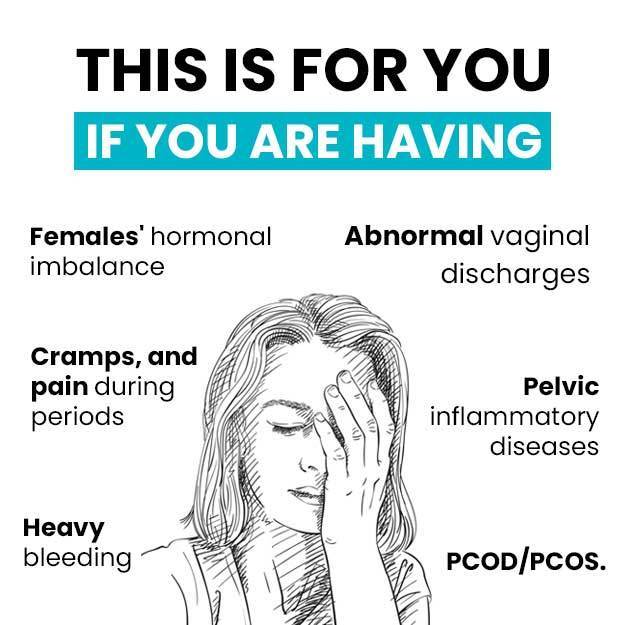
Hypomenorrhoea, also known as light periods or scanty menses, is a condition where the woman experiences extremely scanty flow during menstruation. It may be associated with a reduced duration of periods too. The total amount of blood discharged from the body in hypomenorrhea is less than 80 ml and may last for less than two days. Some of the causes of hypomenorrhea include heredity, pregnancy, low-fat content in the body, hormonal imbalance, and polycystic ovary syndrome. It can also be due to certain contraceptive methods, such as birth control pills and intrauterine devices. The commonly used diagnostic methods to detect hypomenorrhea are blood tests and ultrasound scanning. This condition is generally managed by treating the cause.
(Read more: Heavy periods causes)