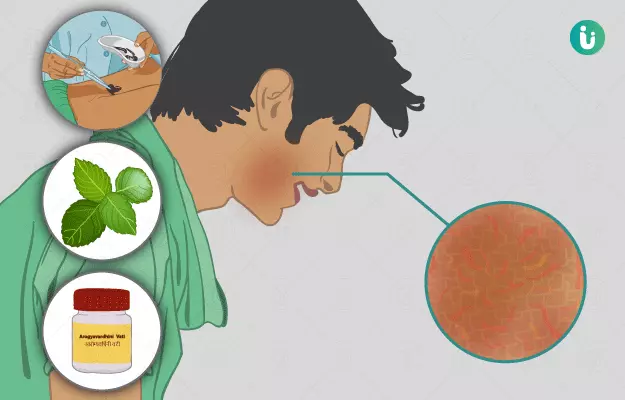
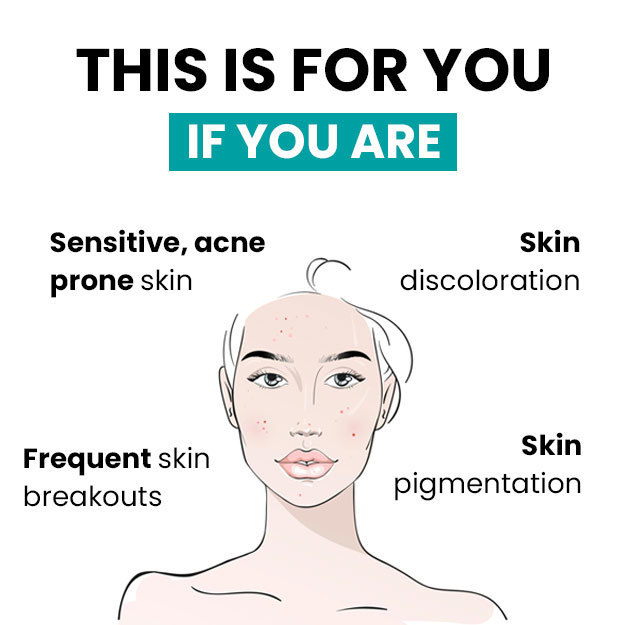
Eczema, known as vicharchika in Ayurveda, is a non-contagious and inflammatory disease of the skin that causes itching and redness of the affected areas. The redness also spreads to the unaffected parts around the inflamed area. Eczema can be acute or chronic, though the cause of the condition is not yet known to conventional medicine.
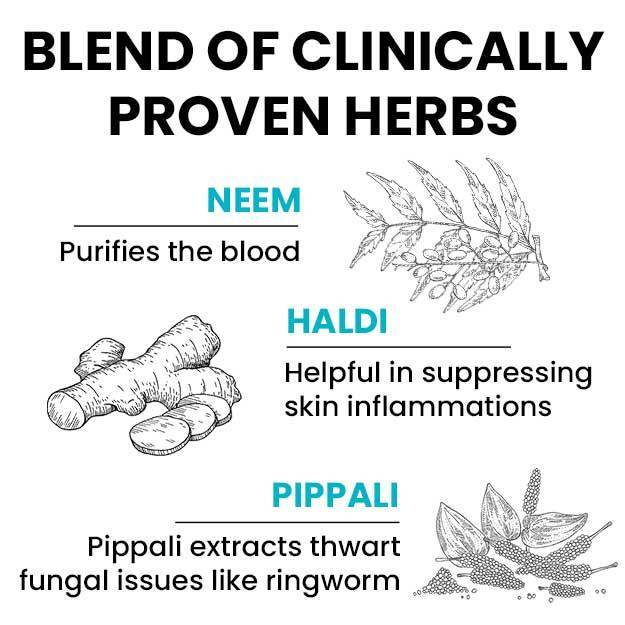
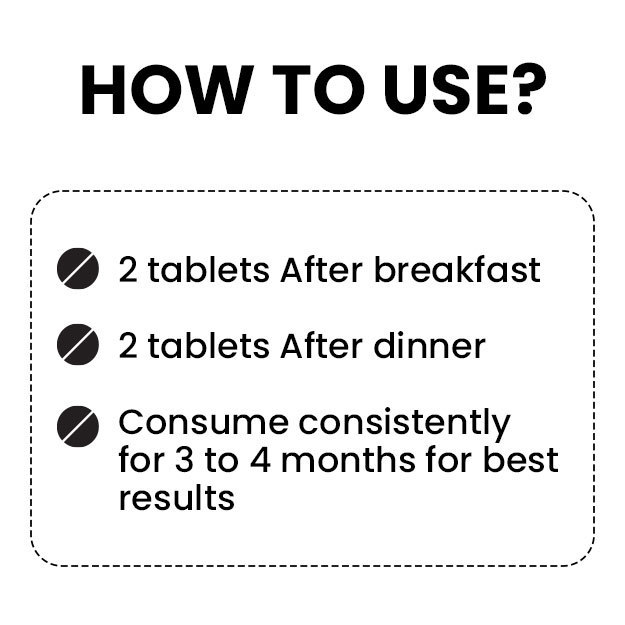
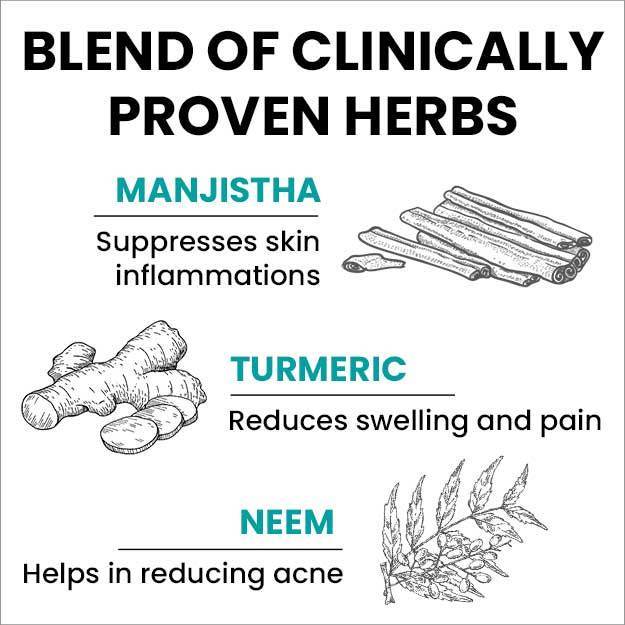
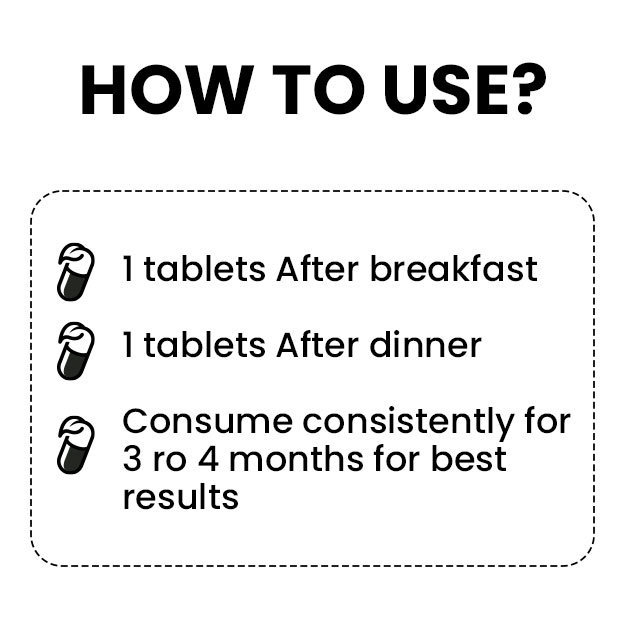
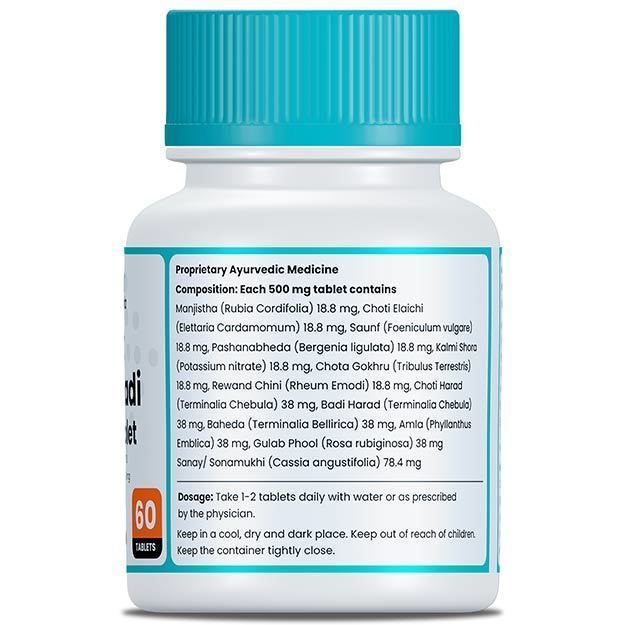
Ayurveda identifies the causes of eczema and describes various treatments like abhyanga (oil massage), vamana (medical emesis), virechana (purgation therapy), rakta mokshana (bloodletting) and lepa (coating the affected body part with medications). Herbs such as neem, haridra (turmeric), kumari (aloe vera) and bakuchi (psoralea) have been used in Ayurveda for their therapeutic effects on eczema. The medicines prescribed by Ayurvedic doctors for treating eczema include arogyavardhini vati, mahatiktaka ghrita, gandhaka rasayana, avalgujadi lepa and rasakarpoora lepa.