Pregnancy brings a lot of changes in a woman’s body. The mom-to-be's organs work overtime to fulfil the needs of the expecting mother and the growing baby. Indeed, there are certain medical conditions like thyroid problems and gestational diabetes which can arise during pregnancy.
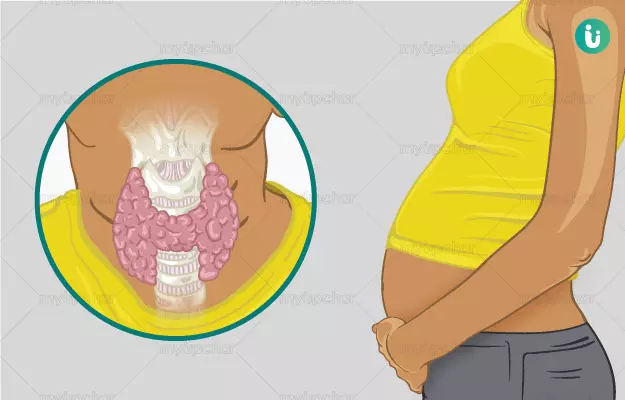
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland present in the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. It helps to regulate body functions like heart rate, body temperature and metabolism by releasing a steady amount of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) into the bloodstream. Thyroid dysfunction can present itself either as hyperthyroidism or as hypothyroidism.
Hypothyroidism is marked by decreased production of thyroxine (T4), which cause the metabolism to slow down, thus leading to weight gain.
Hyperthyroidism occurs when your thyroid gland produces too much of the hormone thyroxine which accelerates the body’s metabolism and may lead to various changes in the body including weight loss.
Thyroid hormone is critical during pregnancy as it is needed for the development of the baby’s brain and nervous system. The foetus depends entirely on the mother for thyroid hormone throughout the first trimester of pregnancy as the baby's thyroid begins to work only after the 12th week of pregnancy. The baby gets the mother’s thyroid hormone through the placenta.
Read more: Yoga for Thyroid Problems
If you are tired of dieting and exercising and are not able to lose weight, then use myUpchar Ayurveda Medarodh Fat Burner Capsule, it has no side effects, order it today and avail the benefits.