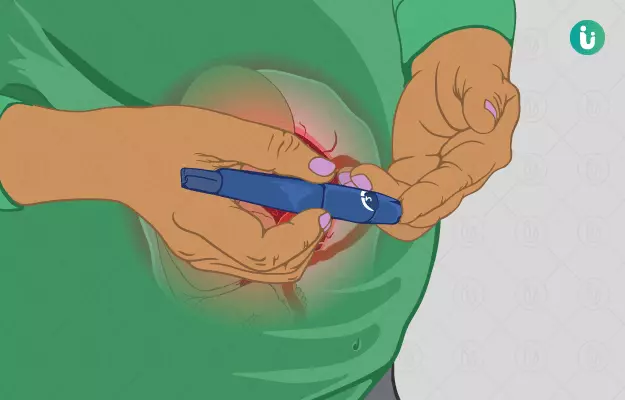
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which the level of sugar in a woman's blood increases during pregnancy. This happens in about 4% of pregnancies. It is usually diagnosed in the later stages of pregnancy and often occurs in women who do not have pre-diabetes.
Gestational diabetes is caused by hormonal and other changes during pregnancy. Our body converts food into energy with the help of insulin. When insulin levels are low, or the body is unable to use insulin effectively (i.e., insulin resistance), blood glucose levels rise.
Please click on the link given here to know the treatment for diabetes.
Gestational diabetes should be diagnosed and treated as soon as possible as it can lead to complications for both the mother and the baby. This increases the risk of pre-eclampsia, depression, and the need for surgery.
This can be avoided by keeping the weight under control and exercising regularly before pregnancy. Gestational diabetes can be treated with a proper diet. Regular exercise can contribute to controlling glucose.
Today in this article you will know in detail about gestational diabetes -
(Read More - Diabetes Myths and Facts)